# 13. PyTorch 笔记
# 1. 安装
安装包比较大,建议先配置清华源,参考第一章 Python 环境🔗
进入 Pytorch 官网的 安装页面🔗 (opens new window), 根据需要选择环境和安装版本

根据生成的命令再本地执行安装
比如根据上图选择的通过 pip 安装的适用于 python 的 cpu 版本 Pytorch
pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio1使用 gpu 进行训练需要配置 cuda 环境,参考 CUDA 安装🔗
- Tips1: gpu 版本需要先 NVIDIA 显卡并安装 CUDA,最好先根据列出的版本安装对应的 CUDA 版本,比如上图要安装 CUDA11.1,然后复制对应的指令安装相应版本的 torch
- Tips2: 安装包比较大,可以通过 pip 指令列出的地址下载好安装包后,从本地安装
import torch print(torch.cuda.is_available()) # True 表示可用 # 显示显卡数量 print(torch.cuda.device_count()) # 1 表示只有一块显卡 # 显示当前 print(torch.cuda.current_device()) # 0 表示当前在第一块显卡上 # 显示显卡名 print(torch.cuda.get_device_name(0)) # NVIDIA GeForce MX150 # 实际使用 GPU 进行训练的方法 device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") # 有 GPU 就用 GPU, 否则用 CPU model.to(device) # 移动模型到 GPU x_data = x_data.to(device) # 将训练数据放入 GPU y_data = y_data.to(device) # 将训练数据放入 GPU out = model(x_data) # 进行训练1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# 2. 基础使用方法
# 2.1. 数据处理
数据转换
# torch 转 numpy torch_data.numpy() # numpy 转 torch torch_data = torch.FloatTensor(np_data).to(device) # 或 torch_data = torch.tensor(np_data, dtype=torch.float32, device=device)1
2
3
4
5
6
7降维
torch.squeeze(input, dim=None, out=None)1numpy 转 tensor
x = torch.from_numpy(x) # numpy 转 tensor1DataLoader 用法
import torch.utils.data as Data # x, y 分别为数据集的输入和输出 x = torch.from_numpy(x.astype(np.float32)) # numpy 转 tensor.float32 y = torch.from_numpy(y.astype(np.float32)) # numpy 转 tensor.float32 torch_dataset = Data.TensorDataset(x, y) # 转换成 Torch 能识别的 Dataset loader = Data.DataLoader( dataset=torch_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, # 是否打乱数据 num_workers=2, # 多线程读取数据 )1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# 2.2. 创建模型(以全链接为例)
创建模型方法 1:神经网络层与其他层分开写
class MLP(nn.Module): # 模型 def __init__(self): super(MLP, self).__init__() # 继承 nn.Module.__init__() # super().__init__() # 与上面一句等效 self.nn1 = nn.Linear(10, 100) # 第一层线性层,输入 10 维,输出 100 维 self.nn2 = nn.Linear(100, 100) # 第二层线性层 self.nn3 = nn.Linear(100, 10) # 第三层线性层 def forward(self, x): # 第一层 x = self.nn1(x) # 线性 x = torch.relu(x) # 激活函数 x = F.dropout(x, p=0.1, training=self.training) # dropout # 第二层 x = torch.relu(self.nn2(x)) # 另一种写法:线性+激活函数 x = torch.dropout(x, p=0.1, train=self.training) # dropout # 第三层 x = torch.dropout(torch.tanh(self.nn3(x)), p=0.1, train=self.training) # 线性+激活+dropout return x model = MLP() print(model) """ MLP( (nn1): Linear(in_features=10, out_features=100, bias=True) (nn2): Linear(in_features=100, out_features=100, bias=True) (nn3): Linear(in_features=100, out_features=10, bias=True) ) """1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30创建模型方法 2:神经网络层与其他层写到一起
import torch.nn as nn class MLP(nn.Module): # 模型 def __init__(self): super(MLP, self).__init__() # 继承 nn.Module.__init__() # super().__init__() # 与上面一句等效 self.model = nn.Sequential( # 序列 nn.Linear(10, 100), # 第一层线性层,输入 10 维,输出 100 维 nn.ReLU(), # 激活函数 nn.Dropout(0.1), nn.Linear(100, 100), # 第二层线性层 nn.ReLU(), # 激活函数 nn.Dropout(0.1), nn.Linear(100, 10), # 第三层线性层 nn.ReLU(), # 激活函数 nn.Dropout(0.1), ) def forward(self, x): x = self.model(x) return x model = MLP() # 创建模型 print(model) # 打印模型结构,结果如下: """ MLP( (model): Sequential( (0): Linear(in_features=10, out_features=100, bias=True) (1): ReLU() (2): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False) (3): Linear(in_features=100, out_features=100, bias=True) (4): ReLU() (5): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False) (6): Linear(in_features=100, out_features=10, bias=True) (7): ReLU() (8): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False) ) """1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
# 2.3. 模型保存与加载
保存模型
# 只保存模型参数,体积小,速度快 torch.save(net.state_dict(), 'model_para') # 保存完整的模型 torch.save(net, 'model_name')1
2
3
4
5加载模型
map_location 不设置的话,模型会加载到保存模型的设备
# 加载模型参数 model = xxxNet() # 先创建模型 static_dict = torch.load('model_para', map_location='cuda:0') # 加载模型参数文件 model.load_state_dict(static_dict) # 将模型参数加载到模型中 # 加载整个模型 model = torch.load('model_name') model = torch.load('model_name', map_location=torch.device('cpu')) # 加载模型到 cpu1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# 3. Torch 模型
# 3.1. 卷积层 Convolution Layers
卷积层:conv2d 二维卷积,卷积动画🔗 (opens new window)
import torch nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True, padding_mode='zeros', device=None, dtype=None) # in_channels: 输入维度 # out_channels: 输出维度 # kernel_size: 内核维度 # stride: 偏移量 # padding: 填充(矩阵边缘填充的维度) F.conv2d(input, weight, bias=None, stride=1, padding=0) # input: 输入 # weight: 卷积核 # bias: 偏置(相当于加一个常量) # stride: 偏移量 # padding: 填充(矩阵边缘填充的维度)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# 3.2. 池化层 Pooling Layers
池化层:maxpool2d 二维最大池化,减小数据维数,加快训练速度
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size, stride=None, padding=0, dilation=1, return_indices=False, ceil_mode=False) # kernel_size: 池化维度 # stride: 偏移量,默认值=kernel_size # padding: 填充 # dilation: 空洞卷积 # ceil_mode: True=ceil 模式,false=floor 模式1
2
3
4
5
6
# 3.3. 线性层 Liner Layers
线性层(全链接)
# in_features: 输入维数 # out_features: 输出维数 # bias: 是否学习偏置量 nn.Linear(in_features, out_features, bias=True, device=None, dtype=None)1
2
3
4
# 3.4. 激活函数 Non-liner Activations
非线性激活
nn.ReLU(inplace=False) # 0 if x < 0 else x nn.Sigmoid() nn.Tanh()1
2
3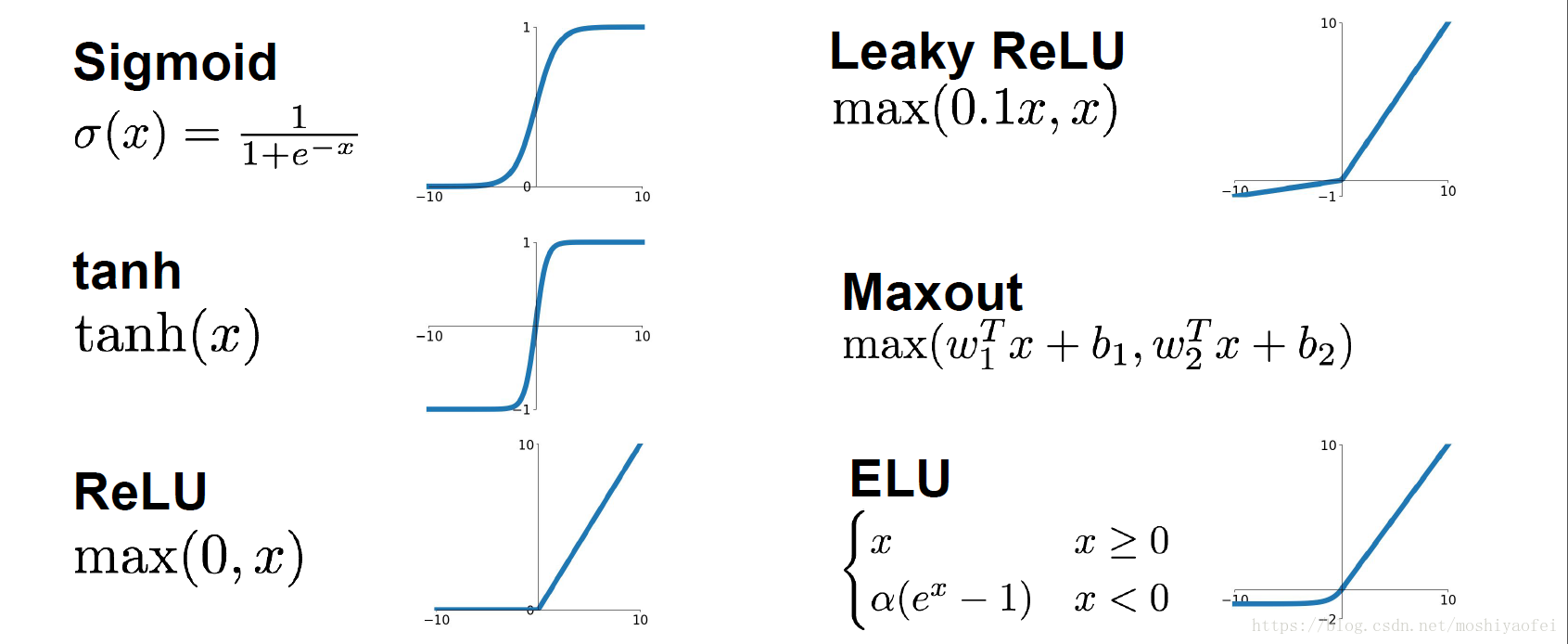
# 3.5. 早停法 EarlyStopping
早停类定义
class EarlyStopping: """ Early stopping to stop the training when the loss does not improve after certain epochs. """ def __init__(self, patience=5, min_delta=0): """ :param patience: how many epochs to wait before stopping when loss is not improving :param min_delta: minimum difference between new loss and old loss for new loss to be considered as an improvement """ self.patience = patience self.min_delta = min_delta self.counter = 0 self.best_loss = None self.early_stop = False def __call__(self, val_loss): if self.best_loss is None: self.best_loss = val_loss elif self.best_loss - val_loss > self.min_delta: self.best_loss = val_loss # reset counter if validation loss improves self.counter = 0 elif self.best_loss - val_loss < self.min_delta: self.counter += 1 print(f"INFO: Early stopping counter {self.counter} of {self.patience}") if self.counter >= self.patience: print('INFO: Early stopping') self.early_stop = True1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32使用
# 首先在外部定义早停类 early_stopping = EarlyStopping() # 在 epoch 训练的循环内根据 loss 进行早停,也可以将 loss 换成其他观测值 early_stopping(train_loss) if early_stopping.early_stop: break1
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 4. 实例
# 4.1. 全链接神经网络
基础 MLP
import torch import torch.nn as nn # import torch.nn.functional as F import torch.utils.data as Data import pandas as pd import numpy as np from sklearn import preprocessing class MLP(nn.Module): # 创建 MLP 模型 def __init__(self): super(MLP, self).__init__() # 继承 nn.Module.__init__() self.model = nn.Sequential( # 序列 nn.Linear(60, 1000), # 第一层线性层,输入 60 维,输出 100 维 nn.ReLU(), # 激活函数 nn.Dropout(0.2), nn.Linear(1000, 2000), # 第二层线性层 nn.ReLU(), # 激活函数 nn.Dropout(0.2), nn.Linear(2000, 1000), # 第三层线性层 nn.ReLU(), # 激活函数 nn.Dropout(0.1), nn.Linear(1000, 500), # 第四层线性层 nn.Tanh(), # 激活函数 nn.Linear(500, 60) # 第五层输出层 ) def forward(self, x): output = self.model(x) return output def train(): m_model = MLP() m_model.to(device) # 移动模型到 GPU print(m_model) lossfunc = nn.MSELoss() # 损失函数 optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(m_model.parameters(), learning_rate) # 优化器 x, y, y_o = get_data() x = torch.from_numpy(x.astype(np.float32)) # numpy 转 tensor y = torch.from_numpy(y.astype(np.float32)) # numpy 转 tensor torch_dataset = Data.TensorDataset(x, y) # 转换成 Torch 能识别的 Dataset loader = Data.DataLoader( dataset=torch_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, # 是否打乱数据 num_workers=2, # 多线程读取数据 ) for epoch in range(epochs): train_loss = 0 for i, (batch_x, batch_y) in enumerate(loader): train_x = batch_x.cuda() train_y = batch_y.cuda() # print(batch_x.size()) optimizer.zero_grad() # 清空上一步的残余更新参数值 out = m_model(train_x) loss = lossfunc(out, train_y) # 计算误差 loss.backward() # 误差反向传播,计算参数更新值 optimizer.step() # 将参数更新值施加到 net 的 parameters 上 train_loss += loss.data train_loss = train_loss / len(loader) print(f"Epoch {epoch + 1} : Train_loss = {train_loss:.6f}")1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
# 5. 图神经网络 GNN
# 5.1. 图神经网络基础
图神经网络概述
图卷积网络 (Graph Convolutional Networks) 作为最近几年兴起的一种基于图结构的广义神经网络,因为其独特的计算能力,受到了学术界和工业界的关注与研究。传统深度学习模型如 LSTM 和 CNN 在欧式空间中表现不俗,却无法直接应用在非欧式数据上。为此,研究者们通过引入图论中抽象意义上的“图”来表示非欧式空间中的结构化数据,并通过图卷积网络来提取(graph)的拓扑结构,以挖掘蕴藏在图结构数据中的深层次信息。
图神经网络(Graph Neural Network)是一种专门处理图结构数据的神经网络,目前被广泛应用于推荐系统、金融风控、生物计算中。图神经网络的经典问题主要有三种,包括节点分类、连接预测和图分类三种。🔗 (opens new window)
常见图神经网络
网络 名称 备注 GCN 图卷积网络 适用于无向图,不带边信息 GAT 图注意力网络
# 5.2. 图种类
- 无向图
- 异构图
- 带边信息的图
- 动态图
- 多维图
# 5.3. PyTorch 构建 GNN
GCN
import torch from torch import nn class GCN(nn.Module): def __init__(self, *sizes): super().__init__() self.layers = nn.ModuleList([ nn.Linear(x, y) for x, y in zip(sizes[:-1], sizes[1:]) ]) def forward(self, vertices, edges): # ----- 构建邻接矩阵 ----- # 从自我连接开始 adj = torch.eye(len(vertices)) # 边包含连接的定点:[vertex_0, vertex_1] adj[edges[:, 0], edges[:, 1]] = 1 adj[edges[:, 1], edges[:, 0]] = 1 # ----- 前向数据传递 ----- for layer in self.layers: vertices = torch.sigmoid(layer(adj @ vertices)) return vertices1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# 5.4. 图神经网络库 torch_geometric 安装
简易方法 [推荐],根据
Quick Start选择相应的版本和系统,复制下面的 pip 指令安装即可,如果没有列出合适的版本,也可以自行修改 pip 指令中的版本号进行安装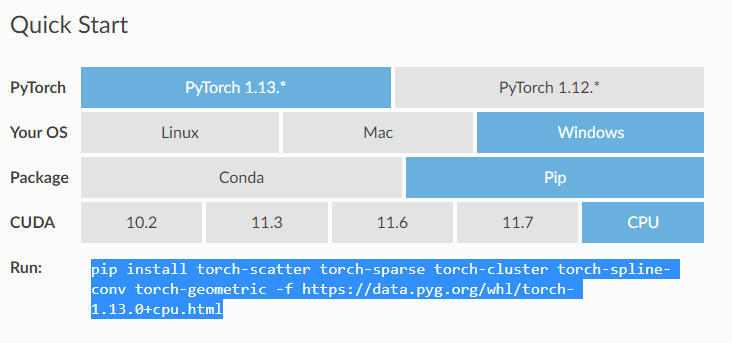
如果在
Quick Start没有找到对应版本可以用如下方法- 找到 Installation 界面,点击图片中的
here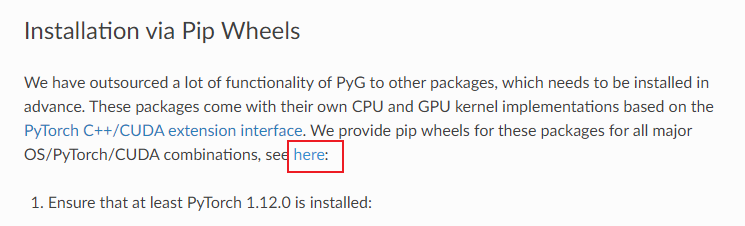
- 根据自己的 torch 版本和系统选择相应的文件夹,比如要安装 CPU 版本,torch=1.13.0, 就点击相应的
torch-1.13.0+cpu版本 - 根据 python 版本下载相应的 whl 文件,比如
Windows 平台,python=3.9要找到cp39-win_amd64.whl后缀的文件,需要安装的文件有 4 个:torch_cluster,torch_scatter,torch_sparse,torch_spline_conv, 不过缺少torch-geometric包,还是需要通过一方法的 pip 安装 - 下载完成后,在要安装的 python 环境中用 pip 指令安装
- 找到 Installation 界面,点击图片中的
# 5.5. torch_geometric 使用
数据示例
from torch_geometric.datasets import KarateClub # 引入数据集 dataset = KarateClub() data = dataset[0] # x = [样本,每个样本的特征维度], edge_index=[样本关系,关系个数], y=[标签], train_mask=[有无标签] # 即 [点数,点的特征], [边,边数] print(data) # Data(x=[34, 34], edge_index=[2, 156], y=[34], train_mask=[34])1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8论文分类实例(可直接运行,需要下载数据集,数据集无法下载时可手动下载然后放入对应目录)
import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F import torch_geometric.nn as gnn from torch_geometric.datasets import Planetoid from torch_geometric.transforms import NormalizeFeatures class GCN(nn.Module): # 模型 def __init__(self, hidden): super().__init__() # 第一层 GCNConv(1433, 16):每个点的特征维度,隐藏层 self.conv1 = gnn.GCNConv(dataset.num_features, hidden) # 第二层 GCNConv(16, 7):隐藏层,输出维度(分类数) self.conv2 = gnn.GCNConv(hidden, dataset.num_classes) def forward(self, x, edge_index): x = self.conv1(x, edge_index) x = x.relu() x = F.dropout(x, p=0.5, training=self.training) x = self.conv2(x, edge_index) return x def train(): # 训练 model.train() optimizer.zero_grad() out = model(data.x, data.edge_index) loss = criterion(out[data.train_mask], data.y[data.train_mask]) loss.backward() optimizer.step() return loss def test(): # 测试 model.eval() out = model(data.x, data.edge_index) pred = out.argmax(dim=1) test_correct = pred[data.test_mask] == data.y[data.test_mask] test_acc = int(test_correct.sum()) / int(data.test_mask.sum()) return test_acc if __name__ == '__main__': # 数据集:2708 个节点,每个节点 1433 个特征,10556 条边 dataset = Planetoid(root='../data/Planetoid', name='Cora', transform=NormalizeFeatures()) # Data(x=[2708, 1433], edge_index=[2, 10556], y=[2708], train_mask=[2708], val_mask=[2708], test_mask=[2708]) data = dataset.data print(f"data_x shape = {data.x.shape}") # torch.Size([2708, 1433]) print(f"edge_index shape = {data.edge_index.shape}") # torch.Size([2, 10556]) model = GCN(hidden=16) print(model) optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.01, weight_decay=5e-4) criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss() for epoch in range(100): los = train() print(f"Epoch {epoch}, Loss={los:.4f}") test_out = test() print(f"Test out accuracy: {test_out:.4f}")1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
# 5.6. torch_geometric 数据集
数据集结构
- data.x: 节点属性矩阵,特征 [节点数,节点特征维度]
- data.edge_index:边信息 [2, 边数量]
创建数据集
from torch_geometric.data import Data # 创建数据集 data = Data(x=torch.from_numpy(feat.astype(np.float32)), edge_index=torch.tensor(edges, dtype=torch.long)) # 给数据集增加新的附加数据,这里增加了训练集的序号和标签,也可自行添加其他数据,名字随意 data.train_index = train[:, 0] data.train_label = train[:, 1]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
