# 6. Matplotlib, Pyecharts 绘图
# 1. 安装
本篇主要是 Python 绘图方法的笔记,以 matplotlib 为主,还包含 seaborn,pyecharts 等模块
安装 Matplotlib🔗 (opens new window)
pip install matplotlib1安装 seaborn🔗 (opens new window)
pip install seabron1安装 Pyecharts, Pyecharts 绘图会保存成 HTML 文件,需要用浏览器打开
pip install pyecharts1
# 2. 绘图种类
# 2.1. plot 折线绘图
代码
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.figure() # 两条曲线 (x1,x2) 和 (x2, y2) plt.plot(x1, y1, x2, y2) plt.show()1
2
3
4
5
6plot 设置,更多设置参考 官方文档🔗 (opens new window)
plt.plot([1, 2, 3], [1, 1, 1], 'b-', label='line 1', linewidth=2) # 蓝色直线 plt.plot([1, 2, 3], [2, 2, 2], 'g--', label='line 2', linewidth=2) # 绿色虚线 plt.plot([1, 2, 3], [3, 3, 3], 'ro-.', label='line 3', linewidth=2) # 红色带圈点划线 plt.plot([1, 2, 3], [4, 4, 4], 'cv:', label='line 4', linewidth=2) # 蓝绿色倒三角点线 plt.plot([1, 2, 3], [5, 5, 5], 'm^', label='line 5', linewidth=2) # 紫红色正三角 plt.plot([1, 2, 3], [6, 6, 6], 'y<', label='line 5', linewidth=2) # 黄色左三角 plt.plot([1, 2, 3], [7, 7, 7], 'k>', label='line 5', linewidth=2) # 黑色右三角1
2
3
4
5
6
7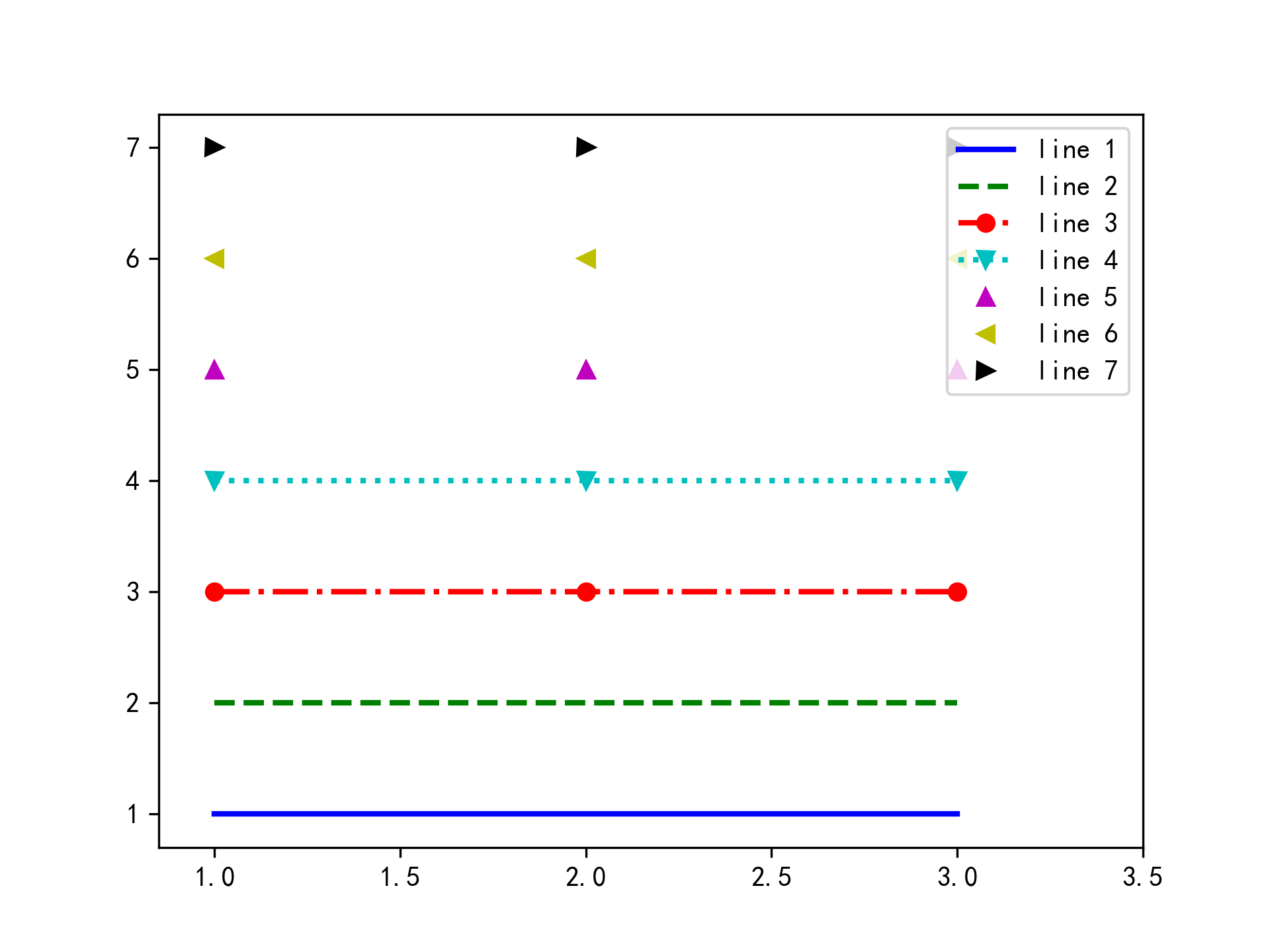
# 2.2. scatter 散点图
带颜色区分的散点图
三维散点图
fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.add_subplot(projection='3d') ax.scatter(x, y, z) ax.set_xlabel('x') ax.set_ylabel('y') ax.set_zlabel('z') plt.show()1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# 2.3. bar 柱状图
基础柱状图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x = list('abcd') y = [1, 2, 3, 4] plt.figure() plt.bar(x, y) plt.show()1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8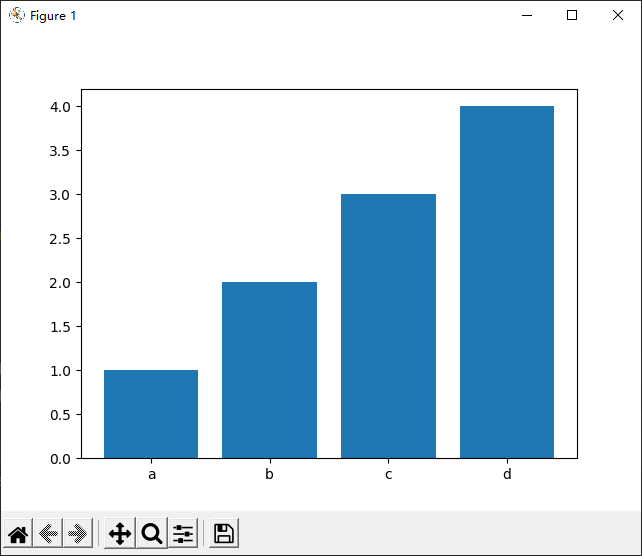
分组柱状图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np fig, ax = plt.subplots() width = 0.1 x = np.arange(0, 3) y1 = [1, 2, 3] y2 = [3, 2, 1] # 用偏移量设置多组柱状图 b1 = ax.bar(np.add(x, -width / 2), y1, width, label='1') b2 = ax.bar(np.add(x, width / 2), y2, width, label='2') ax.legend() # 显示图例 ax.bar_label(b1, padding=3) # 柱状图显示数值 ax.bar_label(b2, padding=3) # 柱状图显示数值 fig.tight_layout() # 减小图片边框 # x 轴间隔设置为 1 x_locator = plt.MultipleLocator(1) ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(x_locator) plt.show()1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24堆叠柱状图
import numpy as np from matplotlib import pyplot as plt x = [1, 2, 3] y1 = [1, 2, 3] y2 = [3, 2, 1] fig, ax = plt.subplots() ax.bar(x, y1, label='a') ax.bar(x, y2, bottom=y1, label='b') ax.legend() plt.show()1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12参数
bar(x, height, width=0.8, bottom=None, ***, align='center', data=None, **kwargs)1参数 功能 x x 坐标 height 高度,即 y 值 width 柱宽,取值在 0-1 之间,默认 0.8 bottom 柱状图的起始位置 align 柱状图的中心位置,'edge'左边缘,'center'中心 动态柱宽
有时需要根据数据设置柱状图列宽和偏移量,下面给出推荐设置
def plot(x, y): # 要求是等间距 x 坐标 delta = x[1] - x[0] # 图像向右偏移半个坐标(柱状图位于两个坐标正中) # 动态柱宽 0.9 * delta 比较好看,可以根据需求适当调整 plt.bar(np.array(x) + 0.5 * delta, y, width=0.9 * delta)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 2.4. pie 饼图
代码
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt labels = 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd' sizes = [15, 30, 45, 10] explode = (0, 0.1, 0, 0) plt.subplots() # explode: 每个楔子偏离的距离 # autopct: 自动显示饼图百分比 plt.pie(sizes, explode=explode, labels=labels, autopct='%1.1f%%', shadow=True, startangle=90) plt.axis('equal') # Equal aspect ratio ensures that pie is drawn as a circle. plt.show()1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13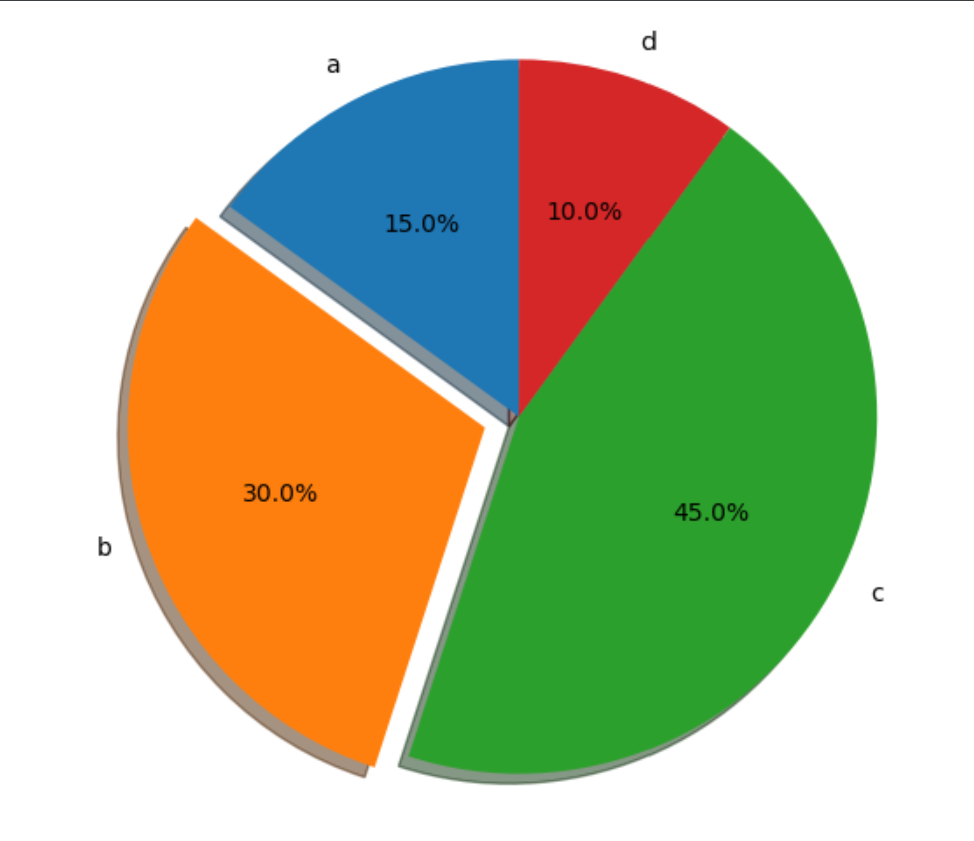
# 2.5. stackplot 堆叠面积图
堆叠面积曲线
x = [1, 2, 3] stacks = { 'A': [1, 2, 3], 'B': [2, 2, 1], 'C': [2, 1, 2] } fig, ax = plt.subplots() ax.stackplot(x, stacks.values(), labels=stacks.keys()) ax.legend() plt.show()1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# 2.6. 盒须图/箱形图
violinplot 提琴图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np # Random test data np.random.seed(19680801) all_data = [np.random.normal(0, std, size=100) for std in range(1, 4)] # [100]*3 数组 labels = ['x1', 'x2', 'x3'] # 均值和中位数只能二选一,False 可以不设置 plt.violinplot(all_data, showmeans=True, # 显示均值 showmedians=False) # 不显示中位数 plt.xticks([x + 1 for x in range(len(all_data))], labels=labels) plt.show()1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
盒须图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np # Random test data np.random.seed(19680801) all_data = [np.random.normal(0, std, size=100) for std in range(1, 4)] labels = ['x1', 'x2', 'x3'] plt.boxplot(all_data) plt.xticks([x + 1 for x in range(len(all_data))], labels=labels) plt.show()1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# 2.7. heatmap 热力图
代码
# 热力图 fig, ax = plt.subplots() im = ax.imshow(df) ax.set_xticks(np.arange(len(df.columns)), labels=df.columns) # 坐标显示成文字 ax.set_yticks(np.arange(len(df.index)), labels=df.index) # 坐标显示成文字 # 热力图中显示数值 for i in range(len(df.index)): for j in range(len(df.columns)): ax.text(j, i, df.iloc[i, j], ha="center", va="center", color="w") # color bar cbar = ax.figure.colorbar(im, ax=ax) cbar.ax.set_ylabel('Pearson 相关性', rotation=-90, va="bottom") # color bar 标题 fig.tight_layout() plt.show()1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17推荐 seaborn 的用法,更加简洁
import seaborn as sns fig, ax = plt.subplots() sns.heatmap(data=df, annot=True) plt.setp(ax.get_xticklabels(), rotation=30, ha="right", rotation_mode="anchor") plt.show()1
2
3
4
5
6
# 3. 图片设置
# 3.1. 坐标轴
坐标轴反向
ax.invert_xaxis() # x 坐标轴反向1设置坐标值
# 按照需求设置坐标,坐标一定要有对应的数据 x_axis = ['2018-09-01', '2018-10-01', '2018-11-01', '2018-12-01', '2018-12-31'] plt.xticks(x_axis, rotation=15) # 刻度倾斜 # 还可以对坐标重命名 x_axis = ['2022-07-25 00:00:00', '2022-07-25 04:00:00', '2022-07-25 08:00:00', '2022-07-25 12:00:00', '2022-07-25 16:00:00', '2022-07-25 20:00:00', '2022-07-26 00:00:00'] plt.plot(df['tm'], final) plt.xticks(x_axis, (0, 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24)) # 将横坐标值重命名为小时时间 plt.show() # 如果是多图的话需要用 set_sticks, 参考本章 2.3 多图设置 # 按照等间隔数值设置坐标 plt.xticks(np.arange(0, 25, 4)) # 范围 0-25,分度值 4 # 不显示坐标 plt.xticks([]) # 不显示 x 轴坐标 plt.yticks([]) # 不显示 y 轴坐标1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18调整坐标轴间隔
# x 轴间隔设置为 1 x_locator = plt.MultipleLocator(1) ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(x_locator)1
2
3设置坐标限位
# 数值型 plt.xlim(0, 24) plt.ylim(0, 10) # 日期型 plt.xlim(datetime.strptime('2019-05-12', '%Y-%m-%d'), datetime.strptime('2019-05-15', '%Y-%m-%d'))1
2
3
4
5
6设置轴标签
plt.figure() plt.xlabel("x") plt.ylabel("y") # 或 fig, ax = plt.subplots() ax.set_xlabel('x') ax.set_ylabel('y')1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8坐标轴字体大小
plt.figure() plt.tick_params(labelsize=14) # 或 fig, ax = plt.subplots() ax.tick_params(labelsize=14)1
2
3
4
5
6坐标轴坐标倾斜
plt.xticks(x_axis, rotation=15) # 刻度倾斜 # 或 ax.set_xticklabels(labels=x, rotation=-45)1
2
3坐标轴偏移
import numpy as np # 以柱状图为例,+图像右移,-图像左移 plt.bar(np.array(x_list) +- 偏移量,y)1
2
3
4
# 3.2. 图例 & 标题
plt.legend
# 设置图例 plt.plot(x1, y1, label='a') plt.plot(x2, y2, label='b') plt.legend()1
2
3
4位置
loc=string or code位置 string 位置 code 位置 'best' 0 自适应 'upper right' 1 右上↗ 'upper left' 2 左上↖ 'lower left' 3 左下↙ 'lower right' 4 右下↘ 'right' 5 右→ 'center left' 6 左← 'center right' 7 右→(同 rigth) 'lower center' 8 下↓ 'upper center' 9 上↑ 'center' 10 中心 设置图例的显示方式
# 图例显示位置 1, 6 列 plt.legend(loc=1, ncol=6) # 图例显示到图外:loc 此时表示定位点,bbox_to_anchor 表示定位点的位置 # 定位点为图例左上角,偏移位置 x=1.05,y=1.0 plt.legend(loc=2, bbox_to_anchor=(1.05, 1.0), borderaxespad=0.)1
2
3
4
5
6标题
plt.title('图名', size=16)1legend 参数,更多配置参考 官方文档🔗 (opens new window)
# 3.3. 多图设置
subplot(nrows, ncols, index, **kwargs)
plt.subplot(2, 2, 1) # 或 plt.subplot(221) plt.plot(x1, y1) plt.subplot(2, 2, 2) # 或 plt.subplot(222) plt.plot(x2, y2) plt.subplot(2, 2, 3) # 或 plt.subplot(223) plt.plot(x3, y3) plt.subplot(2, 2, 4) # 或 plt.subplot(224) plt.plot(x4, y4) # 如果还需要设置副坐标轴 ax1 = plt.subplot(221) ax1.plot(x1, y1) # 图 1 主坐标 ax1b = ax1.twinx() ax1b.plot(x2, y2) # 图 1 副坐标 ax2 = plt.subplot(222) ax2.plot(x3, y3) # 图 2 主坐标 ax2b = ax2.twinx() ax2b.plot(x4, y4) # 图 2 副坐标 ...1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20subplots
# 1. 类似 subplot 的分图功能 # 1xn 类型 fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2) ax[0].plot(x1, y1) ax[0].set_xticks(x_axis, ('0', '12', '24')) # 修改坐标轴显示 ax[0].set_xlabel('x') # 设置 x 轴标签 ax[0].set_ylabel('y') # 设置 y 轴标签 ax[1].plot(x2, y2) # 其他设置同上 # 2x2 以上 fig, ax = plt.subplots(2, 2) ax[0, 0].plot(x1, y1) ax[1, 0].plot(x2, y2)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# 3.4. 多坐标轴(副坐标轴)
副坐标轴功能
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x1 = list('abcd') x2 = x1 y1 = [1, 2, 3, 4] y2 = [4, 3, 2, 1] fig, ax1 = plt.subplots() ax1.plot(x1, y1, label='a') # 设置 ax2 与 ax1 公用横坐标 ax2 = ax1.twinx() # 第二条线必须指定其他颜色,不然都会和第一条曲线显示相同颜色 ax2.plot(x2, y2, c='r', label='b') plt.title('abc') plt.show()1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17图例融合
使用多坐标轴画图时有个问题是
不同坐标轴间的图例会覆盖,因此需要图例融合,将不同图例合并到一起import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x1 = list('abcd') x2 = x1 y1 = [1, 2, 3, 4] y2 = [4, 3, 2, 1] fig, ax1 = plt.subplots() # 设置 ax2 与 ax1 公用横坐标 l1 = ax1.plot(x1, y1, label='a') ax2 = ax1.twinx() l2 = ax2.plot(x2, y2, c='r', label='b') # 图例融合 lns = l1 + l2 labs = [ln.get_label() for ln in lns] ax1.legend(lns, labs, loc=9) plt.title('abc') plt.show()1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
还有一种方法是不同位置分别显示
# 3.5. 辅助线
水平线
# 水平虚线,高度为 y,从 (xmin,y) 到 (xmax,y) plt.hlines(y, xmin, xmax, linestyle=':')1
2竖直线
# 垂直虚线,从 (x,ymin) 到 (x,ymax) plt.vlines(x, ymin, ymax, linestyle=':')1
2图片方格
plt.grid(True) # 开启方格1
# 3.6. 注释
plt.text() 使用
# plt.text()1
2plt.annotate()
# 3.7. 图片显示/输出设置
中文编码问题
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 解决 plt 中文乱码 plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 用来正常显示坐标轴负号1
2图片大小设置
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (12, 8)1图片保存
# 要放在 plt.show() 前面,不然会变成空白 plt.savefig("Picture.png") # 批量保存图片为防止大量图片占用内存,需要关闭图片 plt.close()1
2
3
4图片边框修改
plt.tight_layout() # 缩小边框空白1
# 4. 动态图
Animation
import matplotlib.animation as ani1
2
# 5. Pyecharts
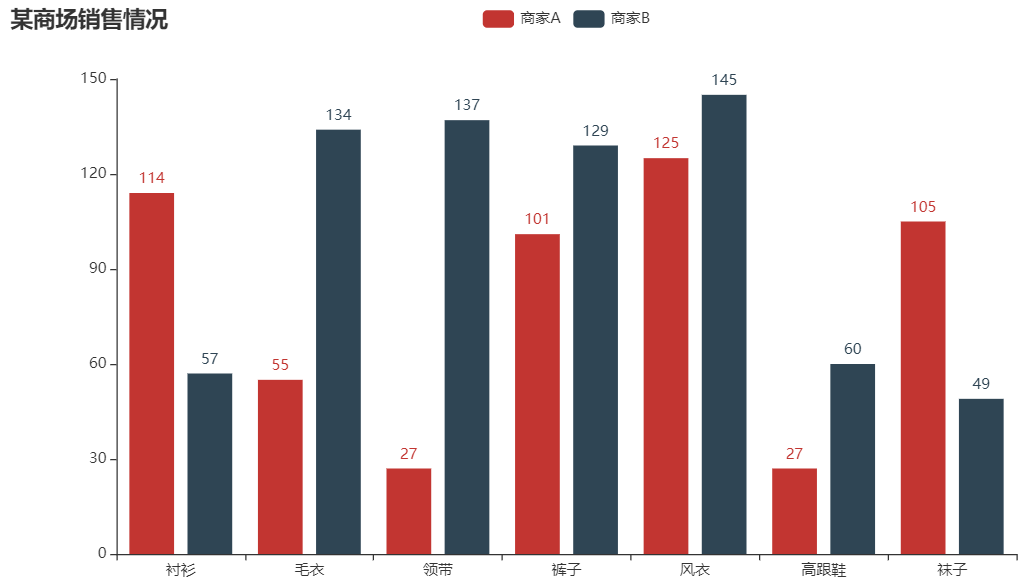
# 5.1. Bar 柱状图
from pyecharts.charts import Bar
from pyecharts import options as opts
bar = (
Bar()
.add_xaxis(["衬衫", "毛衣", "领带", "裤子", "风衣", "高跟鞋", "袜子"])
.add_yaxis("商家 A", [114, 55, 27, 101, 125, 27, 105])
.add_yaxis("商家 B", [57, 134, 137, 129, 145, 60, 49])
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="某商场销售情况"))
.render('render.html')
)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# 5.2. Pie 饼图
from pyecharts.charts import Pie
from pyecharts import options as opts
x = ["衬衫", "毛衣", "领带", "裤子", "风衣", "高跟鞋", "袜子"]
y = [114, 55, 27, 101, 125, 27, 105]
pie = (
Pie()
.add("", [list(x) for x in zip(x, y)])
.set_colors(["blue", "green", "yellow", "red", "pink", "orange", "purple"])
.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(formatter="{b}: {c} ({d}%)"))
.render('render.html')
)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# 6. Pygal
# 6.1. 简介
pygal 是一款动态图表绘制库
安装
pip install pygal1
# 6.2. line
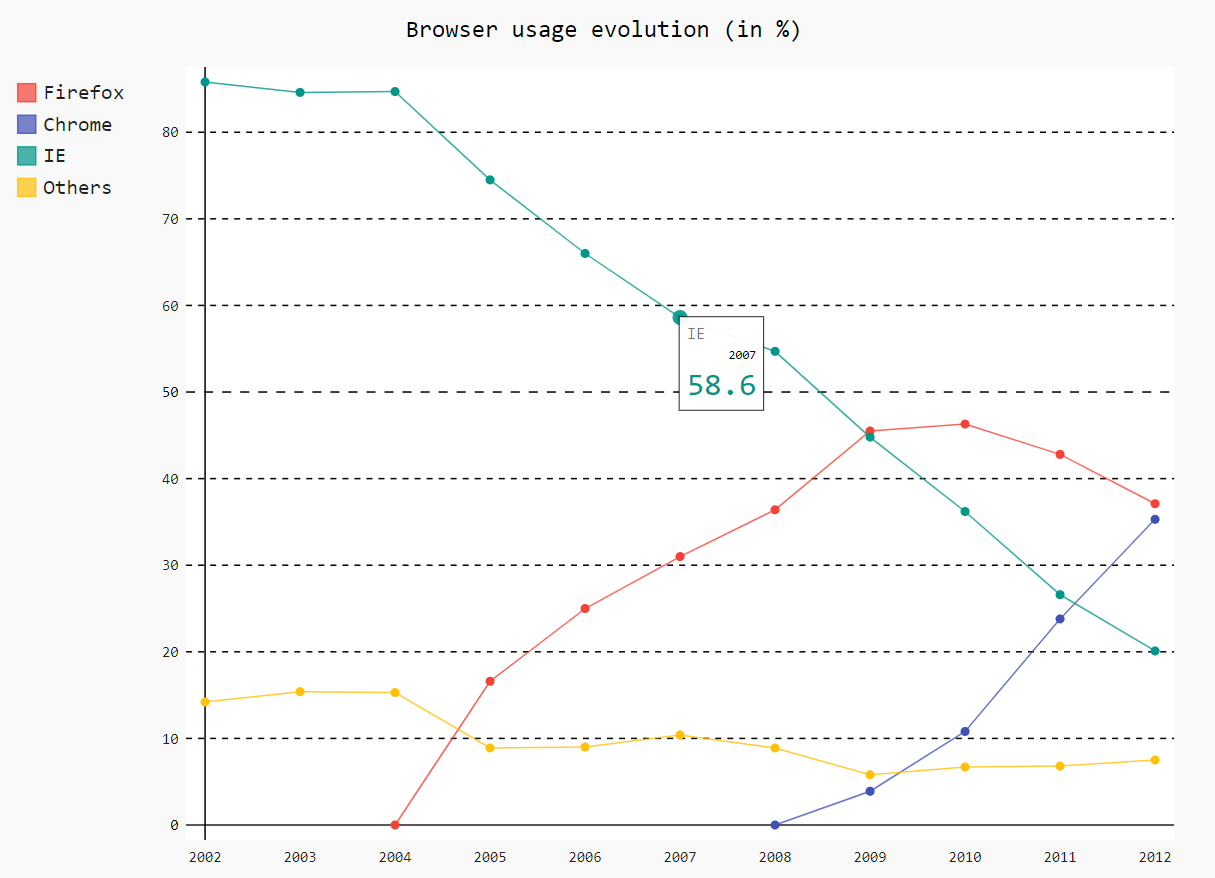
demo
# 官方示例 import pygal line_chart = pygal.Line() line_chart.title = 'Browser usage evolution (in %)' line_chart.x_labels = map(str, range(2002, 2013)) line_chart.add('Firefox', [None, None, 0, 16.6, 25, 31, 36.4, 45.5, 46.3, 42.8, 37.1]) line_chart.add('Chrome', [None, None, None, None, None, None, 0, 3.9, 10.8, 23.8, 35.3]) line_chart.add('IE', [85.8, 84.6, 84.7, 74.5, 66, 58.6, 54.7, 44.8, 36.2, 26.6, 20.1]) line_chart.add('Others', [14.2, 15.4, 15.3, 8.9, 9, 10.4, 8.9, 5.8, 6.7, 6.8, 7.5]) line_chart.render_to_file('line.svg')1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11结果:输出的图片用浏览器打开